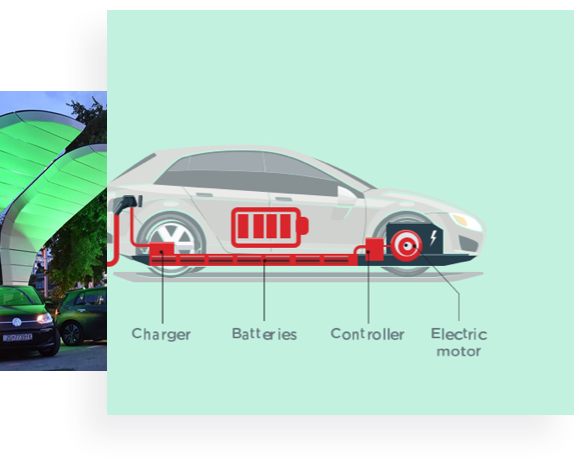
If you’re buying an EV, you should know what’s happening under the hood.
Even the most casual driver can identify the main components of a gas-powered car, like the fuel tank and the engine. And even if you’ve never driven an electric car, it’s still relatively simple to wrap your head around its main parts. For example, instead of a gas tank, they have batteries. Instead of an engine, they have an electric motor. And instead of a tailpipe, they’ve got no tailpipe. Simple, right? Mostly, yes. There are a few other things that a new EV owner should understand.
When you shop for an EV here on MYEVs
We will give you all of the information you need to make an informed decision
like kWh and range and how long it takes to charge a plug-in car. After you read this article, those numbers will make a lot more sense.
Charging
Let’s start with the overall



How do electric Cars Work? The Tesla Model S doesn’t work like other cars. It’s driven by an electric motor and powered by a Lithium-Ion battery. From the AC powered induction engine to the DC charged battery, we go over How the electric cars work! It’s Science!
Bart teaches us how cars work by blowing stuff up and cutting things in half. It’s a science show for the car lover who’s easily bored. Join Bart as he explains the science behind everything automotive. This is cars down to the atom. This is Science Garage.
We are always here for you
Buying your first EV might seem confusing at first. But we are here to help you. Send us any question you have and we will respond as quick as possible with an answer. Sharing our EV knowledge with you. Your questions and our answers will also fill our Learn section which we are already working hard on putting together.
Your MYEV Family
Change Your Location
Weekly graph
FREE ONLINE APPRAISAL